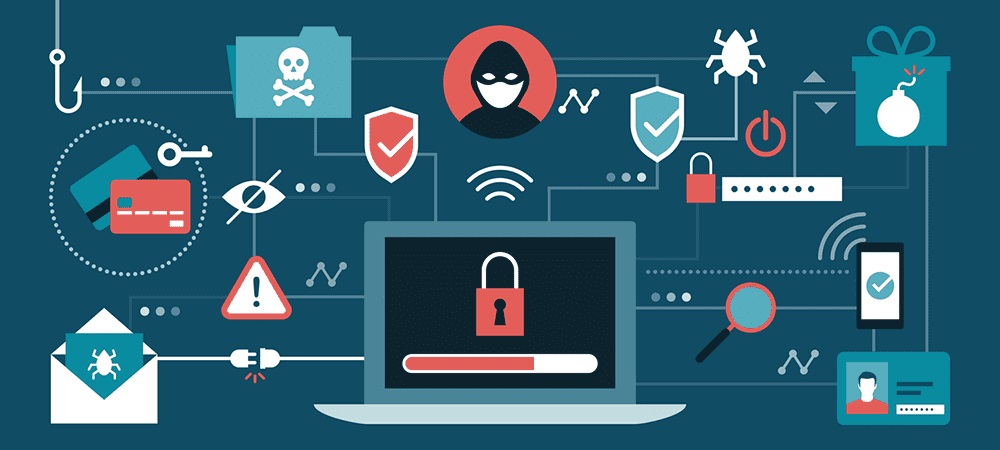
In today’s digital landscape, cyber threats have become increasingly sophisticated, and traditional security measures are no longer enough to safeguard sensitive information and critical systems. As a result, organizations and individuals alike are turning to solutions to fortify their cybersecurity defenses. Advanced malware protection is a comprehensive approach that leverages cutting-edge technologies and strategies to detect, prevent, and mitigate the impact of advanced malware attacks. In this article, we will delve into the significance of advanced malware protection and how it is revolutionizing cybersecurity in the face of relentless cyber threats.
Contents
Understanding Advanced Malware
Advanced malware, also known as advanced persistent threats (APTs), refers to highly sophisticated and stealthy cyber attacks that aim to infiltrate systems, remain undetected, and persistently target valuable data and resources. Unlike traditional malware that operates with limited capabilities, advanced malware is specifically designed to evade detection, manipulate defenses, and carry out long-term attacks.
Key Features of Advanced Malware Protection
It solutions are designed to address the complexities of modern cyber threats and offer a multi-layered defense approach. Some key features of advanced malware protection include
Behavioral Analysis
Advanced malware protection employs behavioral analysis to identify malicious activities and anomalies in real-time. By analyzing the behavior of files, applications, and network traffic, the system can detect unusual patterns and potential threats.
Machine Learning and AI
Machine learning algorithms and artificial intelligence (AI) play a significant role in it. These technologies enable systems to learn from past data and proactively identify emerging threats without relying on predefined signatures.
Sandboxing
Sandboxing is a technique used to isolate suspicious files and run them in a controlled environment to observe their behavior. This allows security teams to analyze potential threats without risking the integrity of the entire system.
Threat Intelligence
It solutions often integrate with threat intelligence feeds, providing real-time information about new threats and vulnerabilities. This helps organizations stay ahead of emerging threats and adapt their defenses accordingly.
Endpoint Security
Protecting endpoints, such as individual devices and servers, is critical in the fight against advanced malware. It includes endpoint security measures to prevent malware from gaining access to these critical access points.
The Advantages of Advanced Malware Protection
Implementing advanced malware protection offers several advantages in the ongoing battle against cyber threats
Early Threat Detection
It can identify threats at an early stage, reducing the chances of a successful cyber attack.
Enhanced Security Posture
By using advanced technologies and strategies, organizations can bolster their security posture and stay one step ahead of evolving cyber threats.
Minimized Downtime and Losses
It helps prevent successful cyber attacks, reducing potential downtime and financial losses associated with data breaches.
Adaptive Defense
The use of machine learning and AI in advanced malware protection allows systems to adapt to new and emerging threats, making them more effective over time.
Compliance and Trust
Implementing robust advanced malware protection measures can enhance an organization’s compliance with data protection regulations and build trust with customers and stakeholders.
As cyber threats continue to evolve and grow in complexity, it is becoming a fundamental aspect of any robust cybersecurity strategy. Leveraging advanced technologies such as behavioral analysis, machine learning, and sandboxing, organizations can proactively defend against advanced malware and other sophisticated cyber threats. By investing in it, businesses and individuals can safeguard sensitive data, protect critical infrastructure, and maintain trust in an increasingly interconnected digital world.