A Nationwide Institute for Fabrics Science (NIMS) analysis staff has succeeded in considerably making improvements to the biking efficiency of a lithium metallic battery by way of growing a automatically very robust polymeric gel electrolyte and integrating it into the battery as a layer to offer protection to the lithium metallic anode. This success would possibly very much facilitate efforts to position lithium metallic anodes—a doubtlessly very top efficiency anode subject matter—into sensible use.
This analysis was once printed in Complex Fabrics.
Lately’s society is impulsively reworking during the fashionable use of virtual applied sciences, the expanding recognition of electrical cars and the rising use of renewable power. Those shifts have created a often emerging call for for upper efficiency lithium secondary batteries. Lithium metallic anodes have very massive theoretical capacities and coffee operating potentials.
Alternatively, in addition they have a topic: the method of lithium dissolution and deposition, which happens because the battery is charged and discharged, is vulnerable to deterioration, shortening the batteries’ charge-discharge cycle lives and posing protection considerations. New applied sciences able to stabilizing the charge-discharge cycles of secondary batteries supplied with lithium metallic anodes are subsequently wanted.
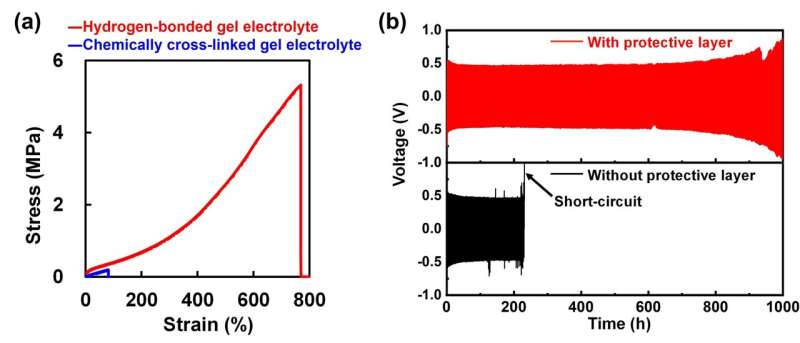
This analysis staff advanced automatically difficult and stretchable gel electrolytes shaped by way of an natural solvent electrolyte containing a top focus of lithium salts and a hydrogen-bonded polymer. The staff then built-in this gel electrolyte as a synthetic layer to offer protection to the lithium metallic anode. Experiments demonstrated that the addition of the protecting layer considerably stepped forward the battery’s biking steadiness.
In long run analysis, the analysis staff plans to optimize the gel electrolyte to be used as a protecting layer and assessment the layer’s effectiveness when mixed with quite a lot of varieties of electrolytes and next-generation cathodes. The staff hopes that this generation will give a contribution to efforts to position next-generation lithium secondary batteries supplied with lithium metallic anodes into sensible use.
Additional info:
Ryota Tamate et al, Extraordinarily Difficult, Stretchable Gel Electrolytes with Sturdy Interpolymer Hydrogen Bonding Ready The use of Concentrated Electrolytes to Stabilize Lithium‐Steel Anodes, Complex Fabrics (2023). DOI: 10.1002/adma.202211679
Quotation:
Extending the lifetime of a lithium metallic anode the use of a protecting layer fabricated from an especially difficult gel electrolyte (2023, Might 9)
retrieved 16 Might 2023
from https://techxplore.com/information/2023-05-life-lithium-metal-anode-layer.html
This record is topic to copyright. With the exception of any honest dealing for the aim of personal find out about or analysis, no
phase is also reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is equipped for info functions best.
Supply By way of https://techxplore.com/information/2023-05-life-lithium-metal-anode-layer.html