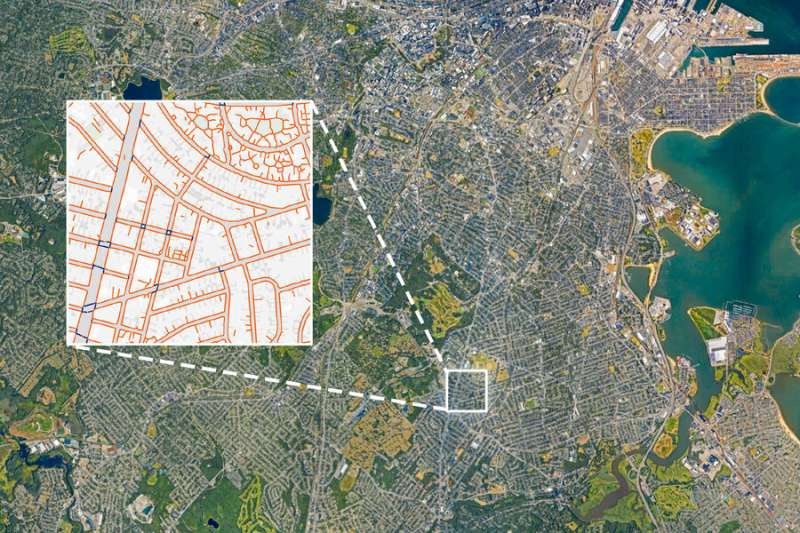
It is more uncomplicated than ever to view maps of anywhere you want to move—by means of automobile, this is. Through foot is any other topic. Maximum towns and cities within the U.S. don’t have sidewalk maps, and pedestrians are normally left to fend for themselves: Are you able to stroll out of your resort to the eating places at the different aspect of the freeway? Is there a shortcut from downtown to the sports activities enviornment? And the way do you get to that bus forestall, anyway?
Now MIT researchers, at the side of colleagues from more than one different universities, have advanced an open-source device that makes use of aerial imagery and image-recognition to create whole maps of sidewalks and crosswalks. The device can lend a hand planners, policymakers, and urbanists who need to increase pedestrian infrastructure.
“Within the city making plans and concrete coverage fields, this can be a massive hole,” says Andres Sevtsuk, an affiliate professor at MIT and a co-author of a brand new paper detailing the device’s functions. “Maximum U.S. town governments know little or no about their sidewalk networks. There is not any information on it. The non-public sector hasn’t taken at the job of mapping it. It gave the look of a truly essential generation to expand, particularly in an open-source method that can be utilized by means of different puts.”
The device, referred to as TILE2NET, has been advanced the usage of a couple of U.S. spaces as preliminary assets of information, however it may be subtle and tailored to be used anyplace.
“We concept we wanted one way that may be scalable and utilized in other towns,” says Maryam Hosseini, a postdoc in MIT’s Town Shape Lab within the Division of City Research and Making plans (DUSP), whose analysis has centered broadly at the building of the device.
The paper, “Mapping the Stroll: A Scalable Pc Imaginative and prescient Manner for Producing Sidewalk Community Datasets from Aerial Imagery,” seems on-line within the magazine Computer systems, Atmosphere and City Programs.
Important analysis for the mission used to be carried out at NYU when Hosseini used to be a pupil there, operating with Silva as a co-advisor.
There are more than one techniques to try to map sidewalks and different pedestrian pathways in towns and cities. Planners may make maps manually, which is correct however time-consuming; or they might use roads and make assumptions in regards to the extent of sidewalks, which would cut back accuracy; or they might check out monitoring pedestrians, which most definitely can be restricted in appearing the total achieve of strolling networks.
As a substitute, the analysis group used automated image-recognition ways to construct a device that can visually acknowledge sidewalks, crosswalks, and footpaths. To try this, the researchers first used 20,000 aerial pictures from Boston, Cambridge, New York Town, and Washington—puts the place complete pedestrian maps already existed. Through coaching the image-recognition style on such obviously outlined gadgets and the usage of parts of the ones towns as a place to begin, they had been in a position to look how smartly TILE2NET would paintings in different places in the ones towns.
In the long run the device labored smartly, spotting 90% or extra of all sidewalks and crosswalks in Boston and Cambridge, for example. Having been educated visually on the ones towns, the device will also be carried out to different metro spaces; folks in different places can now plug their aerial imagery into TILE2NET as smartly.
“We needed to make it more uncomplicated for towns in numerous portions of the arena to do any such factor with no need to do the heavy lifting of coaching [the tool],” says Hosseini. “Collaboratively we will be able to make it higher and higher, with a bit of luck, as we move alongside.”
The desire for any such device is huge, emphasizes Sevtsuk, whose analysis facilities on pedestrian and nonmotorized motion in towns, and who has advanced more than one forms of pedestrian-mapping gear in his occupation. Maximum towns have wildly incomplete networks of sidewalks and paths for pedestrians, he notes. And but it’s exhausting to increase the ones networks successfully with out mapping them.
“Believe that we had the similar gaps in automobile networks that pedestrians have of their networks,” Sevtsuk says. “You may power to an intersection after which the street simply ends. Or you’ll’t take a proper flip since there is not any street. That is what [pedestrians] are continuously up towards, and we do not understand how essential continuity is for [pedestrian] networks.”
Within the nonetheless greater image, Sevtsuk observes, the continuation of local weather exchange signifies that towns must increase their infrastructure for pedestrians and cyclists, amongst different measures; transportation stays an enormous supply of carbon dioxide emissions.
“When towns speak about slicing carbon emissions, there is not any different option to make a large dent than to handle transportation,” Sevtsuk says. “The entire international of city information for public transit and pedestrians and bicycles is truly a ways at the back of [vehicle data] in high quality. Inspecting how towns will also be operational with no automobile calls for this type of information.”
At the brilliant aspect, Sevtsuk suggests, including pedestrian and motorcycle infrastructure “is being executed extra aggressively than in lots of many years previously. Within the twentieth century, it used to be the opposite direction round, we’d remove sidewalks to create space for vehicular roads. We are now seeing the other development. To make perfect use of pedestrian infrastructure, it is crucial that towns have the community information about it. Now you’ll in reality inform how any person can get to a bus forestall.”
Additional info:
Maryam Hosseini et al, Mapping the stroll: A scalable pc imaginative and prescient method for producing sidewalk community datasets from aerial imagery, Computer systems, Atmosphere and City Programs (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2023.101950
This tale is republished courtesy of MIT Information (internet.mit.edu/newsoffice/), a well-liked website that covers information about MIT analysis, innovation and educating.
Quotation:
First open-source device to let planners map pedestrian networks (2023, March 15)
retrieved 18 April 2023
from https://techxplore.com/information/2023-03-open-source-tool-planners-pedestrian-networks.html
This report is matter to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal find out about or analysis, no
section is also reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions best.
Supply Through https://techxplore.com/information/2023-03-open-source-tool-planners-pedestrian-networks.html




