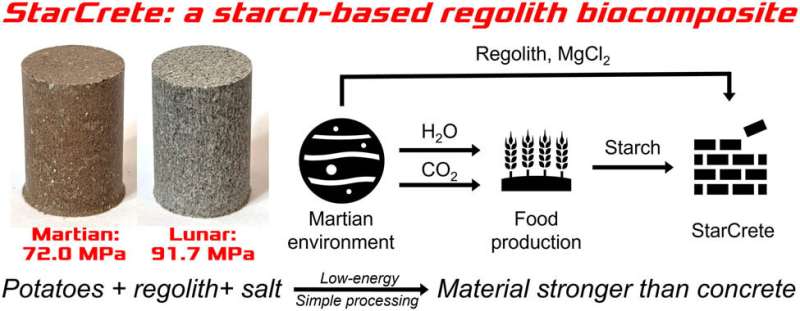
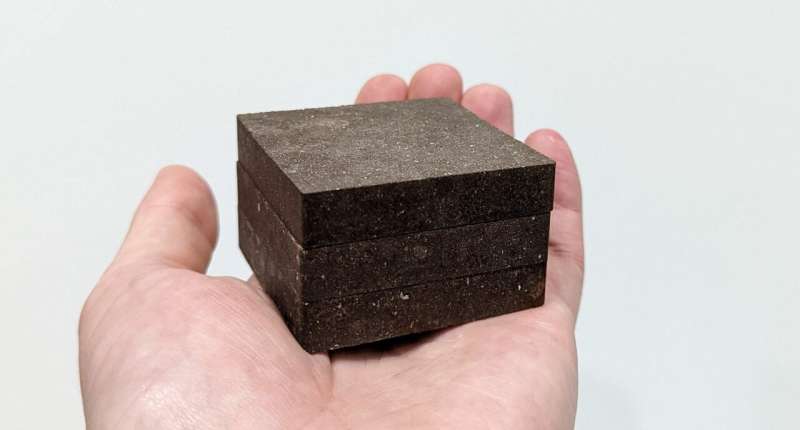
Manchester scientists have created a brand new subject material, dubbed StarCrete, which is constructed from extra-terrestrial mud, potato starch, and a pinch of salt and might be used to construct houses on Mars.
Development infrastructure in house is recently prohibitively dear and tough to reach. Long term house building will wish to depend on easy fabrics which can be simply to be had to astronauts, StarCrete provides one imaginable resolution. The scientists in the back of the discovery used simulated Martian soil combined with potato starch and a pinch of salt to create the fabric this is two times as stable as atypical concrete and is completely suited to building paintings in extra-terrestrial environments.
In a piece of writing printed within the magazine Open Engineering, the analysis staff demonstrated that atypical potato starch can act as a binder when combined with simulated Mars mud to supply a concrete-like subject material. When examined, StarCrete had a compressive energy of 72 Megapascals (MPa), which is over two times as stable because the 32 MPa observed in atypical concrete. Starcrete constructed from moon mud was once even more potent at over 91 MPa.
This paintings improves on earlier paintings from the similar staff the place they used astronauts’ blood and urine as a binding agent. Whilst the ensuing subject material had a compressive energy of round 40 MPa, which is best than standard concrete, the method had the disadvantage of requiring blood frequently. When working in an atmosphere as adverse as house, this feature was once observed as much less possible than the use of potato starch.

“Since we will be able to be generating starch as meals for astronauts, it made sense to take a look at that as a binding agent moderately than human blood. Additionally, present development applied sciences nonetheless want a few years of building and require really extensive power and extra heavy processing apparatus which all provides value and complexity to a challenge. StarCrete does not want any of this and so it simplifies the challenge and makes it inexpensive and extra possible.”
“And anyway, astronauts most definitely do not need to be dwelling in homes constructed from scabs and urine,” mentioned Dr. Aled Roberts, Analysis Fellow on the Long term Biomanufacturing Analysis Hub, and lead researcher for this challenge.
The staff calculate {that a} sack (25 Kg) of dehydrated potatoes (crisps) comprise sufficient starch to supply nearly part a ton of StarCrete, which is identical to over 213 brick’s price of subject material. For comparability, a three-bedroom area takes kind of 7,500 bricks to construct. Moreover, they came upon {that a} not unusual salt, magnesium chloride, out there from the Martian floor or from the tears of astronauts, considerably progressed the energy of StarCrete.
The following phases of this challenge are to translate StarCrete from the lab to utility. Dr. Roberts and his staff have just lately introduced a start-up corporate, DeakinBio, which is exploring tactics to enhance StarCrete in order that it is also utilized in a terrestrial surroundings.
If used on Earth, StarCrete may be offering a greener selection to conventional concrete. Cement and urban account for roughly 8% of world CO2 emissions as the method during which they’re made calls for very top firing temperatures and quantities of power. StarCrete, then again, will also be made in an atypical oven or microwave at standard ‘house baking’ temperatures, due to this fact providing diminished power prices for manufacturing.
Additional information:
Aled D. Roberts et al, StarCrete: A starch-based biocomposite for off-world building, Open Engineering (2023). DOI: 10.1515/eng-2022-0390
Quotation:
Scientists increase a ‘cosmic concrete’ this is two times as stable as steady concrete (2023, March 16)
retrieved 6 April 2023
from https://techxplore.com/information/2023-03-scientists-cosmic-concrete-strong-regular.html
This record is matter to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal find out about or analysis, no
phase is also reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is equipped for info functions handiest.
Supply By means of https://techxplore.com/information/2023-03-scientists-cosmic-concrete-strong-regular.html




